Understanding the AVERAGE Function
Posted 2024-09-03 03:20:32
1
12K
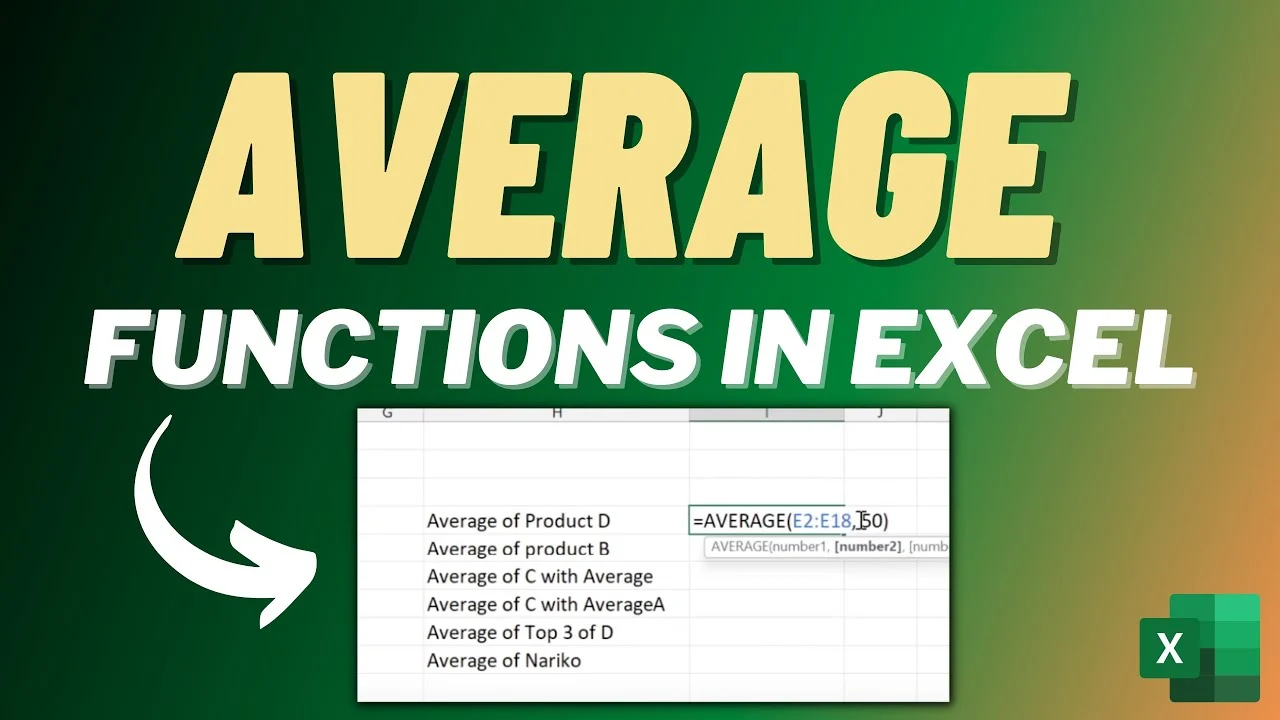
The AVERAGE function in Excel is used to calculate the arithmetic mean of a range of numbers. It's a simple yet powerful tool that can be used in various data analysis scenarios.
Basic Syntax:
Excel
=AVERAGE(number1, [number2], ...)
- number1 (required): The first number or range of numbers to be averaged.
- number2 (optional): Additional numbers or ranges of numbers to be averaged.
Examples:
-
Averaging a Range of Numbers:
- If you have numbers in cells A1 to A10, you can find their average using:
Excel
=AVERAGE(A1:A10)
- If you have numbers in cells A1 to A10, you can find their average using:
-
Averaging Individual Numbers:
- To average specific numbers, you can list them directly in the formula:
Excel
=AVERAGE(10, 20, 30)
- To average specific numbers, you can list them directly in the formula:
-
Combining Ranges and Numbers:
- You can mix ranges and individual numbers:
Excel
=AVERAGE(A1:A5, 100, B2:B4)
- You can mix ranges and individual numbers:
Additional Considerations:
- Text Values: If a cell within the range contains text, it will be treated as 0.
- Error Values: If a cell contains an error (like #DIV/0!), the AVERAGE function will return an error.
- Blank Cells: Blank cells are treated as 0.
- Nested Functions: You can use AVERAGE within other functions. For example, to find the average of only the positive values in a range:
Excel
=AVERAGEIF(A1:A10, ">0", A1:A10)
Advanced Usage:
- Conditional Averaging: Use the AVERAGEIF or AVERAGEIFS functions to average values based on criteria.
- Array Formulas: For complex calculations involving arrays, you can use array formulas with AVERAGE.
Example: Using AVERAGEIF
To average only the values in column B where the corresponding values in column A are greater than 50:
Excel
=AVERAGEIF(A1:A10, ">50", B1:B10)
Key Points to Remember:
- The AVERAGE function calculates the arithmetic mean.
- It can be used with ranges, individual numbers, and other functions.
- Be aware of how the function handles text, errors, and blank cells.
- Explore advanced techniques like AVERAGEIF and array formulas for more complex calculations.


Buscar
Categorías
- Technology
- Educación
- Business
- Music
- Got talent
- Film
- Politics
- Food
- Juegos
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Read More
UACE WAKISSHA PHYSICS PAPER 1 2024
UACE WAKISSHA PHYSICS PAPER 1 2024
Types Summary and Type Conversion
Types summary
The following is a summary of the different Python types:
string -...
Reconstruction (Lecture)
Reconstruction Era (1865-1877)
The Reconstruction Era was a period of immense change and...
Understanding Quadratic Equations:
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree 2. It can be expressed in the general...
Identity Theft
Identity Theft occurs when someone unlawfully obtains and uses another person’s personal...